Last Commit
Mar. 8, 2019
Mar. 8, 2019
Created
Aug. 20, 2017
Aug. 20, 2017
opencv4nodejs
By its nature, JavaScript lacks the performance to implement Computer Vision tasks efficiently. Therefore this package brings the performance of the native OpenCV library to your Node.js application. This project targets OpenCV 3 and provides an asynchronous as well as an synchronous API.
The ultimate goal of this project is to provide a comprehensive collection of Node.js bindings to the API of OpenCV and the OpenCV-contrib modules. An overview of available bindings can be found in the API Documentation. Furthermore, contribution is highly appreciated. If you want to get involved you can have a look at the contribution guide.
- Examples
- How to install
- Usage with Docker
- Usage with Electron
- Usage with NW.js
- Quick Start
- Async API
- With TypeScript
- External Memory Tracking (v4.0.0)
- Available Modules
Examples
See examples for implementation.
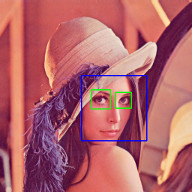
Face Detection
Face Recognition with the OpenCV face module
Check out Node.js + OpenCV for Face Recognition.
Face Landmarks with the OpenCV face module
Face Recognition with face-recognition.js
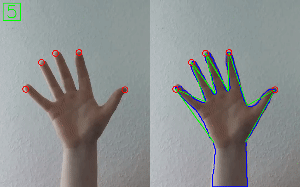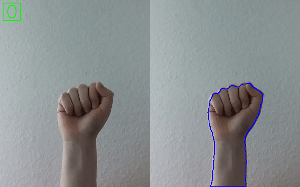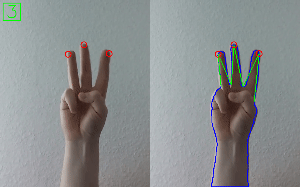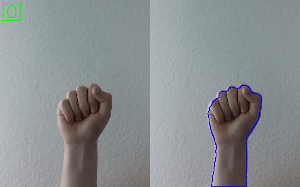
Hand Gesture Recognition
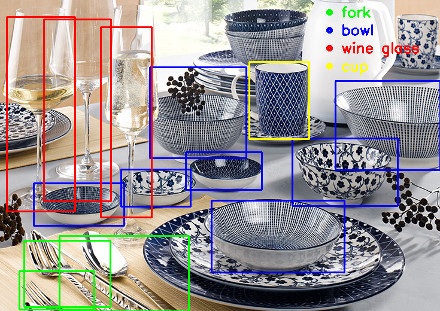
Object Recognition with Deep Neural Networks
Tensorflow Inception
Single Shot Multibox Detector with COCO
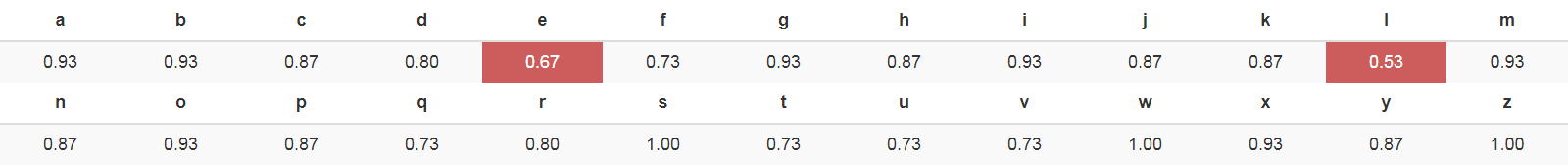
Machine Learning
Check out Machine Learning with OpenCV and JavaScript: Recognizing Handwritten Letters using HOG and SVM.
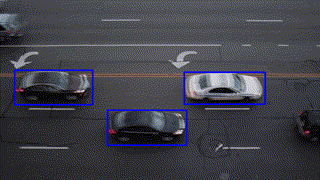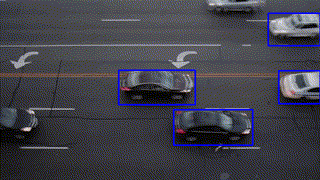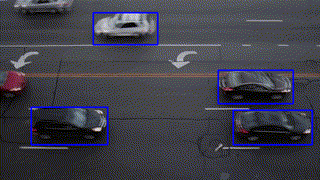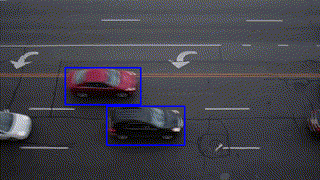
Object Tracking
Feature Matching
Image Histogram
How to install
Important note: node-gyp won't handle whitespaces properly, thus make sure, that the path to your project directory does not contain any whitespaces. Installing opencv4nodejs under "C:\Program Files\some_dir" or similar will not work and will fail with: "fatal error C1083: Cannot open include file: 'opencv2/core.hpp'"!**
Requirements
- cmake (unless you are using a prebuilt OpenCV release)
On Windows
On windows you will need Windows Build Tools to compile OpenCV and opencv4nodejs. If you don't have Visual Studio or Windows Build Tools installed, you can easily install the VS2015 build tools:
npm install --global windows-build-tools
Auto build
If you do not want to set up OpenCV on your own you can simply let this package auto install OpenCV 3.4 + OpenCV contrib 3.4 (might take some time):
$ npm install --save opencv4nodejs
Auto build flags
You can customize the autobuild flags using OPENCV4NODEJS_AUTOBUILD_FLAGS="". Flags must be space-separated.
This is an advanced customization and you should have knowledge regarding the OpenCV compilation flags.
For example
export OPENCV4NODEJS_AUTOBUILD_FLAGS="-DBUILD_LIST=dnn" will build only modules required for dnn and reduced the size of the opencv package. Flags added by default are listed hereManual build
Setting up OpenCV on your own will require you to set an environment variable: OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_AUTOBUILD=1.
You can either install any of the OpenCV 3+ releases (note, this will come without contrib) or build OpenCV with or without OpenCV contrib from source on your own. On Linux and MacOSX the library should be installed under usr/local (which is the default).
On Windows
If you choose to set up OpenCV on your own you have to set the following environment variables before installing opencv4nodejs:
- OPENCV_INCLUDE_DIR pointing to the directory with the subfolders opencv and opencv2 containing the header files
- OPENCV_LIB_DIR pointing to the lib directory containing the OpenCV .lib files
Also you will need to add the OpenCV binaries to your system path:
- add an environment variable OPENCV_BIN_DIR pointing to the binary directory containing the OpenCV .dll files
- append
;%OPENCV_BIN_DIR%;to your system path variable
Note: Restart your current console session after making changes to your environment.
If you are running into issues also check the requirements for node-gyp specific to your OS: https://github.com/nodejs/node-gyp.
Usage with Docker
opencv-express - example for opencv4nodejs with express.js and docker
Or simply pull from justadudewhohacks/opencv-nodejs for opencv-3.2 + contrib-3.2 with opencv4nodejs globally installed:
FROM justadudewhohacks/opencv-nodejs
Note: The aforementioned Docker image already has
opencv4nodejs installed globally. In order to prevent build errors during an npm install, your package.json should not include opencv4nodejs, and instead should include/require the global package either by requiring it by absolute path or setting the NODE_PATH environment variable to /usr/lib/node_modules in your Dockerfile and requiring the package as you normally would.
Different OpenCV 3.x base images can be found here: https://hub.docker.com/r/justadudewhohacks/.
Usage with Electron
opencv-electron - example for opencv4nodejs with electron
Add the following script to your package.json:
"electron-rebuild": "electron-rebuild -w opencv4nodejs"
Run the script:
$ npm run electron-rebuild
Require it in the application:
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Usage with NW.js
Any native modules, including opencv4nodejs, must be recompiled to be used with NW.js. Instructions on how to do this are available in the [Use Native Modules] (http://docs.nwjs.io/en/latest/For%20Users/Advanced/Use%20Native%20Node%20Modules/) section of the the NW.js documentation.
Once recompiled, the module can be installed and required as usual:
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Quick Start
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs');
Initializing Mat (image matrix), Vec, Point
const rows = 100; // height
const cols = 100; // width
// empty Mat
const emptyMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
// fill the Mat with default value
const whiteMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC1, 255);
const blueMat = new cv.Mat(rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3, [255, 0, 0]);
// from array (3x3 Matrix, 3 channels)
const matData = [
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]],
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]],
[[255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0], [255, 0, 0]]
];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(matData, cv.CV_8UC3);
// from node buffer
const charData = [255, 0, ...];
const matFromArray = new cv.Mat(Buffer.from(charData), rows, cols, cv.CV_8UC3);
// Point
const pt2 = new cv.Point(100, 100);
const pt3 = new cv.Point(100, 100, 0.5);
// Vector
const vec2 = new cv.Vec(100, 100);
const vec3 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5);
const vec4 = new cv.Vec(100, 100, 0.5, 0.5);
Mat and Vec operations
const mat0 = new cv.Mat(...);
const mat1 = new cv.Mat(...);
// arithmetic operations for Mats and Vecs
const matMultipliedByScalar = mat0.mul(0.5); // scalar multiplication
const matDividedByScalar = mat0.div(2); // scalar division
const mat0PlusMat1 = mat0.add(mat1); // addition
const mat0MinusMat1 = mat0.sub(mat1); // subtraction
const mat0MulMat1 = mat0.hMul(mat1); // elementwise multiplication
const mat0DivMat1 = mat0.hDiv(mat1); // elementwise division
// logical operations Mat only
const mat0AndMat1 = mat0.and(mat1);
const mat0OrMat1 = mat0.or(mat1);
const mat0bwAndMat1 = mat0.bitwiseAnd(mat1);
const mat0bwOrMat1 = mat0.bitwiseOr(mat1);
const mat0bwXorMat1 = mat0.bitwiseXor(mat1);
const mat0bwNot = mat0.bitwiseNot();
Accessing Mat data
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
const matGray = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC1);
// get pixel value as vector or number value
const vec3 = matBGR.at(200, 100);
const grayVal = matGray.at(200, 100);
// get raw pixel value as array
const [b, g, r] = matBGR.atRaw(200, 100);
// set single pixel values
matBGR.set(50, 50, [255, 0, 0]);
matBGR.set(50, 50, new Vec(255, 0, 0));
matGray.set(50, 50, 255);
// get a 25x25 sub region of the Mat at offset (50, 50)
const width = 25;
const height = 25;
const region = matBGR.getRegion(new cv.Rect(50, 50, width, height));
// get a node buffer with raw Mat data
const matAsBuffer = matBGR.getData();
// get entire Mat data as JS array
const matAsArray = matBGR.getDataAsArray();
IO
// load image from file
const mat = cv.imread('./path/img.jpg');
cv.imreadAsync('./path/img.jpg', (err, mat) => {
...
})
// save image
cv.imwrite('./path/img.png', mat);
cv.imwriteAsync('./path/img.jpg', mat,(err) => {
...
})
// show image
cv.imshow('a window name', mat);
cv.waitKey();
// load base64 encoded image
const base64text='data:image/png;base64,R0lGO..';//Base64 encoded string
const base64data =base64text.replace('data:image/jpeg;base64','')
.replace('data:image/png;base64','');//Strip image type prefix
const buffer = Buffer.from(base64data,'base64');
const image = cv.imdecode(buffer); //Image is now represented as Mat
// convert Mat to base64 encoded jpg image
const outBase64 = cv.imencode('.jpg', croppedImage).toString('base64'); // Perform base64 encoding
const htmlImg=' '
'
Useful Mat methods
const matBGR = new cv.Mat(..., cv.CV_8UC3);
// convert types
const matSignedInt = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_32SC3);
const matDoublePrecision = matBGR.convertTo(cv.CV_64FC3);
// convert color space
const matGray = matBGR.bgrToGray();
const matHSV = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV);
const matLab = matBGR.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2Lab);
// resize
const matHalfSize = matBGR.rescale(0.5);
const mat100x100 = matBGR.resize(100, 100);
const matMaxDimIs100 = matBGR.resizeToMax(100);
// extract channels and create Mat from channels
const [matB, matG, matR] = matBGR.splitChannels();
const matRGB = new cv.Mat([matR, matB, matG]);
Drawing a Mat into HTML Canvas
const img = ...
// convert your image to rgba color space
const matRGBA = img.channels === 1
? img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_GRAY2RGBA)
: img.cvtColor(cv.COLOR_BGR2RGBA);
// create new ImageData from raw mat data
const imgData = new ImageData(
new Uint8ClampedArray(matRGBA.getData()),
img.cols,
img.rows
);
// set canvas dimensions
const canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
canvas.height = img.rows;
canvas.width = img.cols;
// set image data
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.putImageData(imgData, 0, 0);
Method Interface
OpenCV method interface from official docs or src:
void GaussianBlur(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, Size ksize, double sigmaX, double sigmaY = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT);
translates to:
const src = new cv.Mat(...);
// invoke with required arguments
const dst0 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2);
// with optional paramaters
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, 0.8, cv.BORDER_REFLECT);
// or pass specific optional parameters
const optionalArgs = {
borderType: cv.BORDER_CONSTANT
};
const dst2 = src.gaussianBlur(new cv.Size(5, 5), 1.2, optionalArgs);
Async API
The async API can be consumed by passing a callback as the last argument of the function call. By default, if an async method is called without passing a callback, the function call will yield a Promise.
Async Face Detection
const classifier = new cv.CascadeClassifier(cv.HAAR_FRONTALFACE_ALT2);
// by nesting callbacks
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg', (err, img) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const grayImg = img.bgrToGray();
classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg, (err, res) => {
if (err) { return console.error(err); }
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
});
});
// via Promise
cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg')
.then(img =>
img.bgrToGrayAsync()
.then(grayImg => classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg))
.then((res) => {
const { objects, numDetections } = res;
...
})
)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
// using async await
try {
const img = await cv.imreadAsync('./faceimg.jpg');
const grayImg = await img.bgrToGrayAsync();
const { objects, numDetections } = await classifier.detectMultiScaleAsync(grayImg);
...
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
With TypeScript
import * as cv from 'opencv4nodejs'
Check out the TypeScript examples.
External Memory Tracking (v4.0.0)
Since version 4.0.0 was released, external memory tracking has been enabled by default. Simply put, the memory allocated for Matrices (cv.Mat) will be manually reported to the node process. This solves the issue of inconsistent Garbage Collection, which could have resulted in spiking memory usage of the node process eventually leading to overflowing the RAM of your system, prior to version 4.0.0.
Note, that in doubt this feature can be disabled by setting an environment variable
OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING before requiring the module:export OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING=1 // linux
set OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING=1 // windows
Or directly in your code:
process.env.OPENCV4NODEJS_DISABLE_EXTERNAL_MEM_TRACKING = 1
const cv = require('opencv4nodejs')
Available Modules
API doc overview
- core
- io
- imgproc
- ximgproc
- objdetect
- machinelearning
- deepneuralnetworks
- video
- calib3d
- photo
- features2d
- xfeatures2d
- tracking
- text
- face












留言
張貼留言